Thermal power plants are essential facilities that generate electricity by converting heat energy into electrical energy. In this article, we'll explore the workings of thermal power plants, delve into different types, and provide insights into their significance in the energy sector.
1.
Understanding Thermal Power Plants
Thermal
power plants are electricity generation facilities that use heat energy to
produce electricity. They play a crucial role in meeting the growing demand for
electricity worldwide, providing a reliable source of power for various
industrial, commercial, and residential applications.
2.
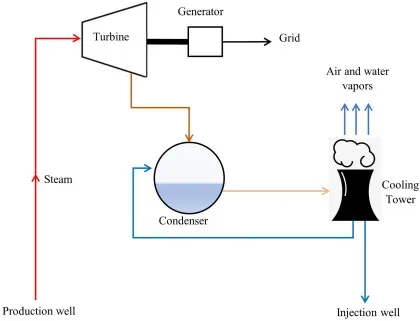
Working Principle of Thermal Power Plants
The
working principle of a thermal power plant involves several key steps:
- Fuel
Combustion: The primary
fuel, such as coal, natural gas, or oil, is burned in a boiler to generate heat
energy.
- Steam
Generation: The heat
produced by fuel combustion is used to convert water into steam.
- Turbine
Rotation: The high-pressure steam drives a
turbine, causing it to rotate.
- Electricity
Generation: The rotating
turbine is connected to a generator, which converts mechanical energy into
electrical energy.
- Cooling
and Condensation: After passing
through the turbine, the steam is condensed back into water in a condenser.
- Water
Recycling: The condensed water is then recycled
back to the boiler to repeat the cycle.
3.
Types of Thermal Power Plants
Coal-fired
Power Plants
Coal-fired
power plants are the most common type of thermal power plants, utilizing coal
as the primary fuel source. These plants are known for their reliability and
affordability but are often criticized for their environmental impact,
including air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
Gas-fired
Power Plants
Gas-fired
power plants use natural gas or liquefied petroleum gas (LPG) as fuel. These
plants are more efficient and produce fewer emissions compared to coal-fired
plants. They are often preferred for their flexibility and quick start-up
times.
Oil-fired
Power Plants
Oil-fired
power plants utilize various types of fuel oils, including diesel and heavy
fuel oil. While less common than coal and gas-fired plants, oil-fired plants
are still used in regions where other fuel sources are limited. They offer
flexibility in fuel selection but are generally more expensive to operate.
4.
Components of a Thermal Power Plant
Boiler
The
boiler is the heart of a thermal power plant, where fuel combustion occurs to
produce high-pressure steam.
Turbine
The
turbine is a rotary mechanical device driven by steam or gas, which converts
kinetic energy into electrical energy.
Generator
The
generator is an electrical device connected to the turbine shaft, converting
mechanical energy into electrical energy through electromagnetic induction.
Condenser
The
condenser is a heat exchanger that cools and condenses the steam back into
water after it passes through the turbine.
Cooling
Tower
The
cooling tower is used to dissipate excess heat from the condenser water, often
through evaporation or direct contact with air or water.
5.
Environmental Impact of Thermal Power Plants
Thermal
power plants can have significant environmental impacts, including air and
water pollution, habitat destruction, and contribution to climate change
through greenhouse gas emissions. Efforts to mitigate these impacts include the
adoption of cleaner technologies, such as carbon capture and storage (CCS) and
renewable energy integration.
6.
Advantages and Disadvantages
Advantages
- Reliable and consistent power generation
- Utilization of diverse fuel sources
- Contribution to economic development and energy security
Disadvantages
- Environmental pollution and degradation
- Dependence on finite fossil fuel resources
- Vulnerability to fuel price fluctuations
7.
FAQs
How
does a thermal power plant generate electricity?
A
thermal power plant generates electricity by converting heat energy into
mechanical energy using steam turbines, which drive electrical generators.
What
are the main types of thermal power plants?
The
main types of thermal power plants include coal-fired, gas-fired, and oil-fired
power plants, each utilizing different fuel sources for electricity generation.
What
are the environmental concerns associated with thermal power plants?
Environmental
concerns associated with thermal power plants include air pollution, water
pollution, habitat destruction, and greenhouse gas emissions, contributing to
climate change.
How
can the environmental impact of thermal power plants be mitigated?
The
environmental impact of thermal power plants can be mitigated through the
adoption of cleaner technologies, such as renewable energy integration, energy
efficiency improvements, and emissions reduction measures.
What
is the future outlook for thermal power plants?
The
future outlook for thermal power plants is influenced by factors such as
technological advancements, regulatory policies, and market trends. Efforts to
transition towards cleaner and more sustainable energy sources are expected to
shape the future of thermal power generation.
Conclusion
Thermal
power plants play a crucial role in meeting global energy demands, providing a
reliable source of electricity for various applications. While they offer
several advantages, including fuel diversity and reliability, they also pose
significant environmental challenges. By embracing cleaner technologies and
adopting sustainable practices, the future of thermal power generation can be
more environmentally friendly and sustainable.



0 Comments