Demystifying Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD)
Exploring CFD Basics
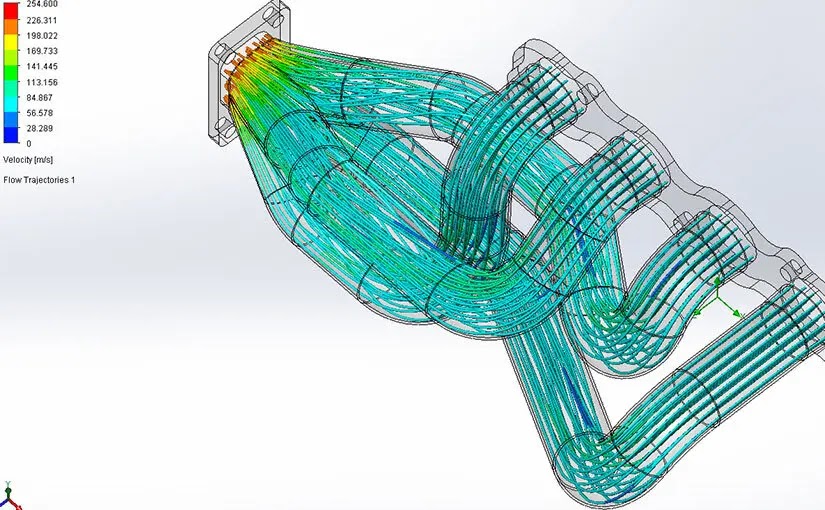
What is CFD?
CFD, or Computational Fluid Dynamics, is a tech tool used to
understand how fluids like air and water move around objects.
How does CFD work?
It uses math and computers to make virtual models of fluid
flow, showing things like air patterns around planes or water flow in pipes.
Real-world Applications
In Aerospace: CFD helps design better airplanes by predicting how air flows
over wings and bodies, making flights smoother and more fuel-efficient.
In Cars: It improves car designs by simulating airflow around vehicles, making
them sleeker for better performance and fuel economy.
For Renewable Energy: CFD optimizes wind turbine designs and layouts, making wind
farms more productive and efficient.
Advantages of CFD
Saves Money: CFD replaces expensive physical tests with virtual
simulations, saving companies time and money during product development.
Offers Insights: It provides detailed insights into fluid behavior, helping
engineers understand how to make things work better.
Optimizes Designs: By tweaking designs in virtual simulations, engineers can
make products like cars and turbines perform better in the real world.
Future Possibilities
Advanced Simulations: As computers get faster, CFD can simulate even more complex
fluid behaviors, opening new doors for innovation.
Integration with AI: Pairing CFD with artificial intelligence can make
simulations smarter and more predictive, revolutionizing how we design and
engineer things.
In essence, Computational Fluid Dynamics simplifies complex
fluid dynamics into understandable simulations, driving innovation across
industries from aerospace to renewable energy.